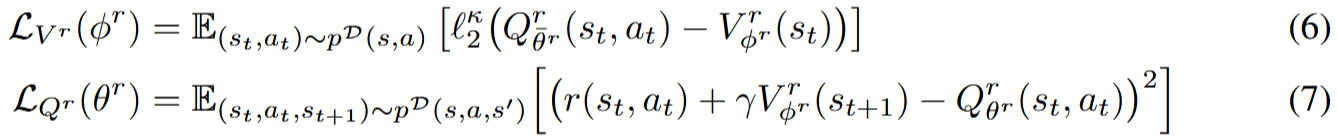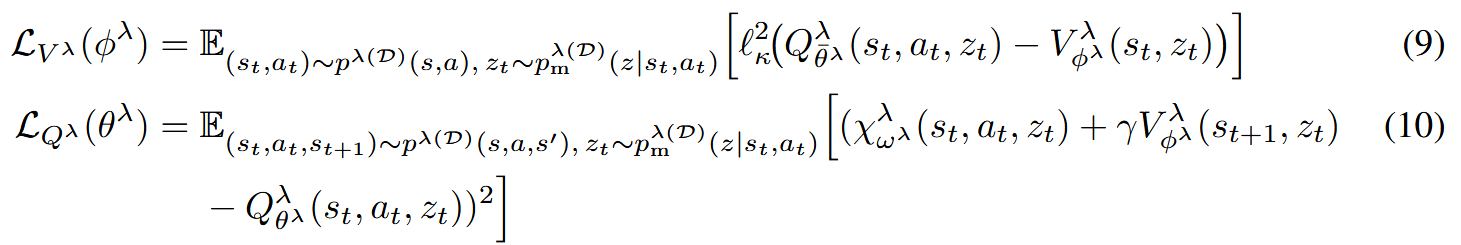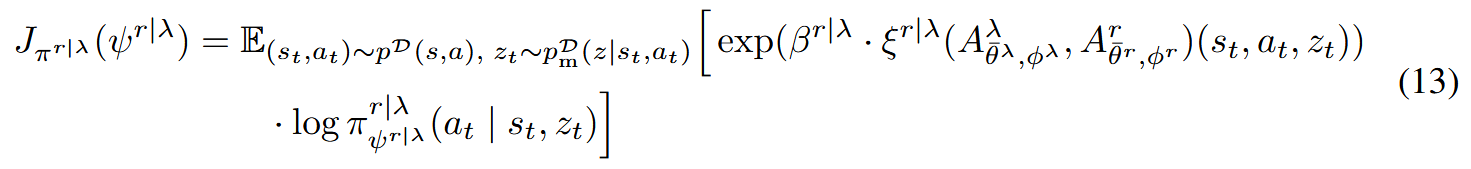We propose a novel general definition of behavior styles within the sequential decision making framework and instantiate it by the use of labeling functions to learn interpretable styles with a low labeling cost and easy alignment measurement while effectively avoiding unnecessary credit assignment issues by relying on subtrajectories labeling.
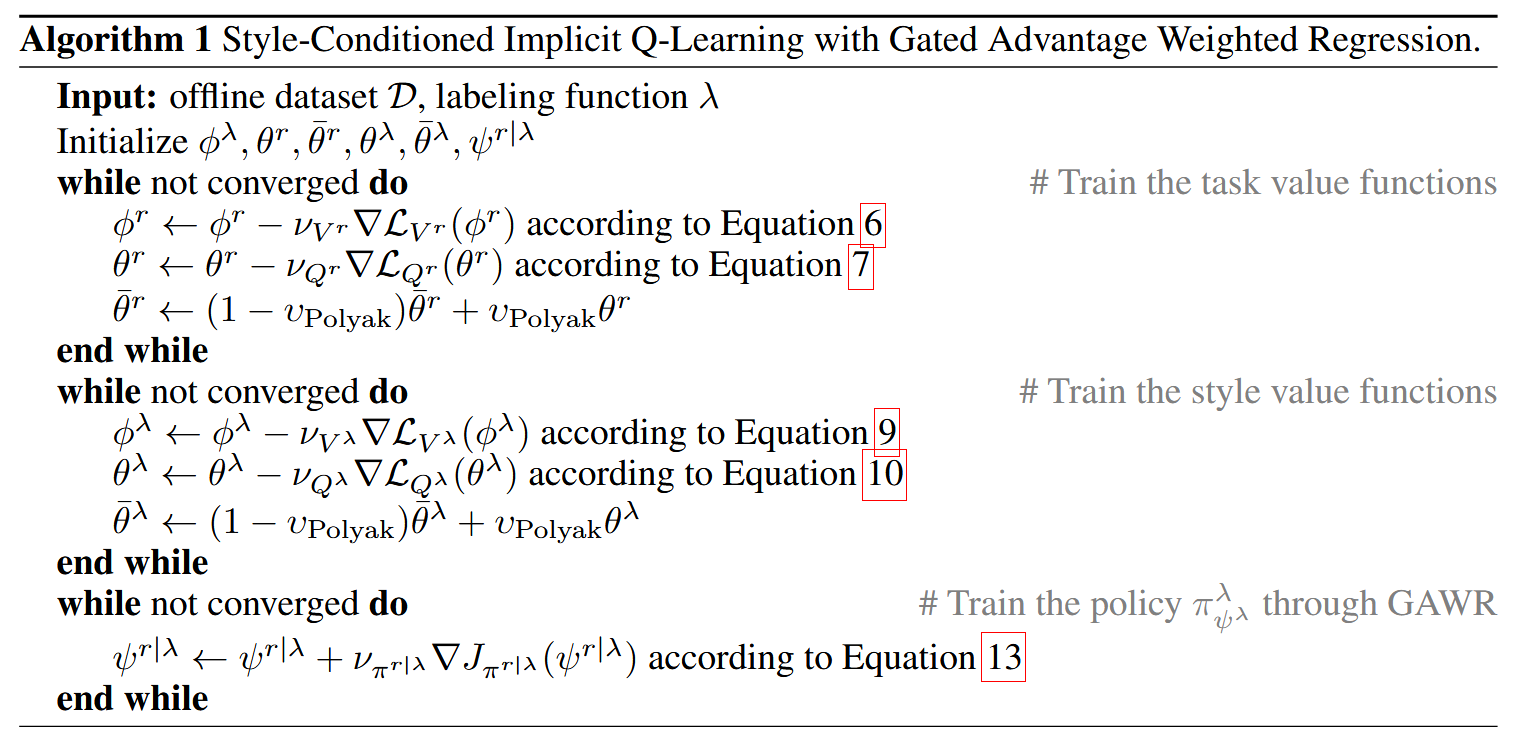
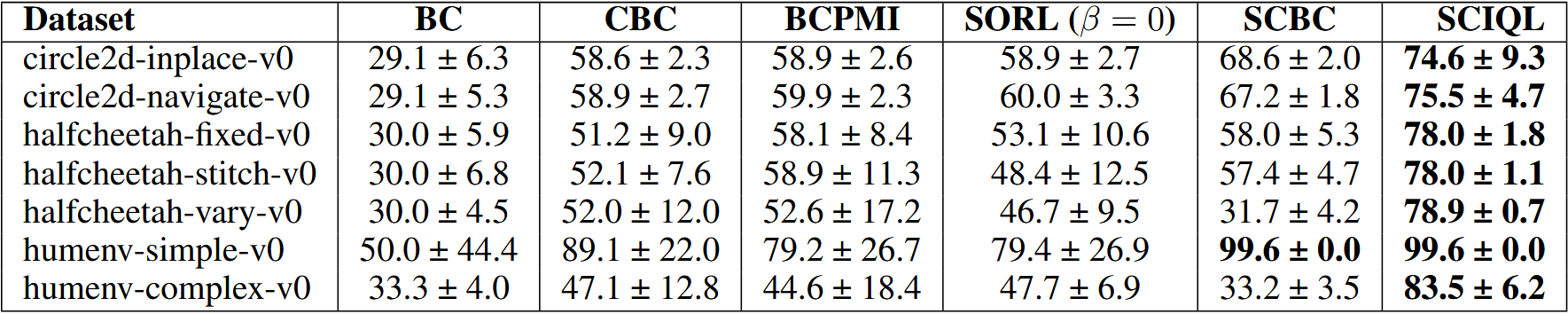
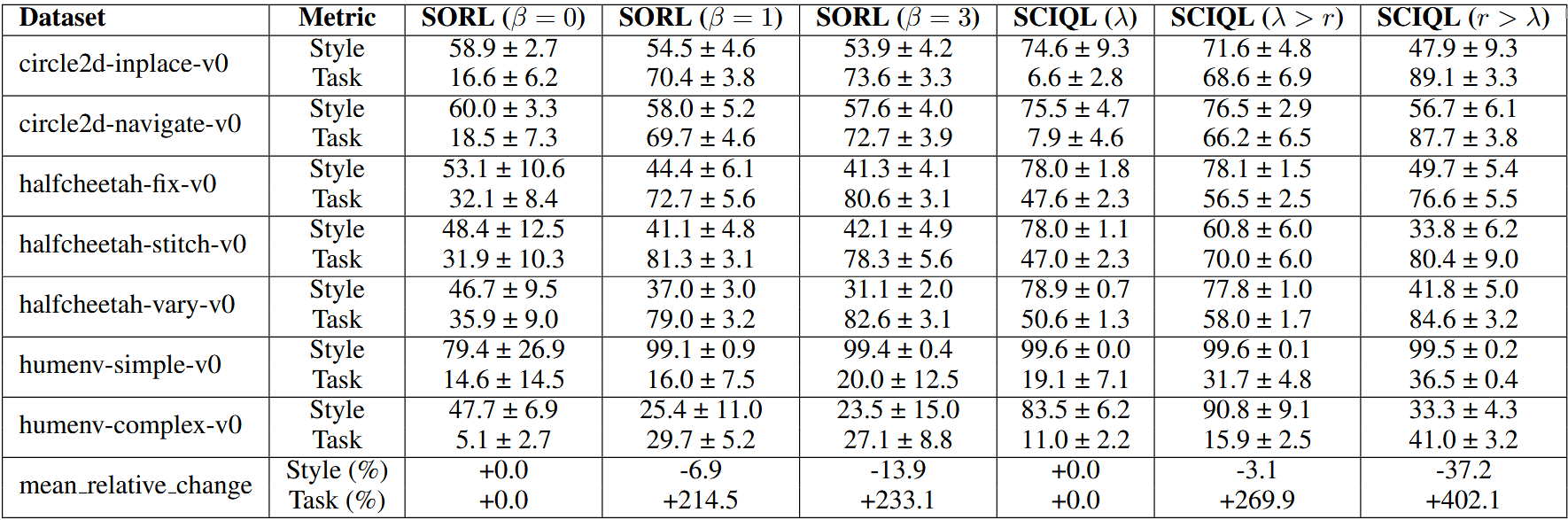
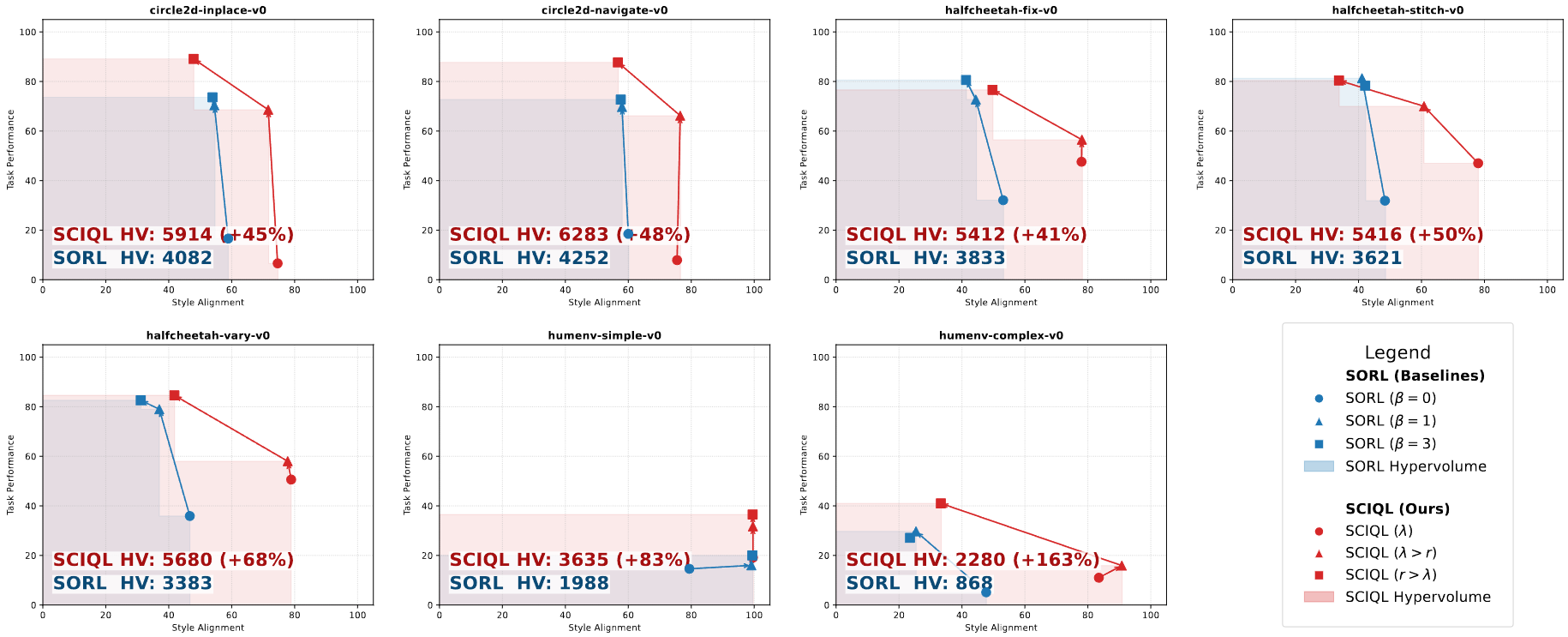
We then present the SCIQL algorithm which leverages Gated AWR to solve long-term decision making and trajectory stitching challenges while providing superior performance in both style alignment and style-conditioned task performance compared to previous work.
We think that our framework opens the door to several interesting research directions:
- Multiplicity of criteria: An interesting next step would be to find ways to scale the framework to a multiplicity of criteria.
- Enhanced representations: Finding mechanisms to enhance the representation span of labeling functions could also be interesting.
- Zero-shot capabilities: Finally, integrating zero-shot capabilities to generate on the fly style-conditioned reinforcement learning policies would be worthwhile to explore.